Herniated Disc
Herniated Disc Treatment at Orthopedic and Spine Centers of Wisconsin
Appointments Available Within 24hrs
What Is a Herniated Disc?
A herniated disc, also known as a slipped or bulging disc, occurs when the soft inner core of a spinal disc pushes through the tough outer layer. This can occur either in the cervical spine (neck) or lumbar spine (lower back) and can lead to pain, numbness, or weakness in the arms or legs, depending on the location of the affected disc.
What Causes a Herniated Disc?
Herniated discs can result from various factors, including:
- Age-related Wear and Tear: Discs degenerate over time, making them more susceptible to herniation.
- Improper Lifting: Incorrect lifting techniques can strain the spine and lead to disc injuries.
- Genetics: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to disc problems.
- Trauma or Injury: Sudden impact or injuries to the spine can cause disc herniation.
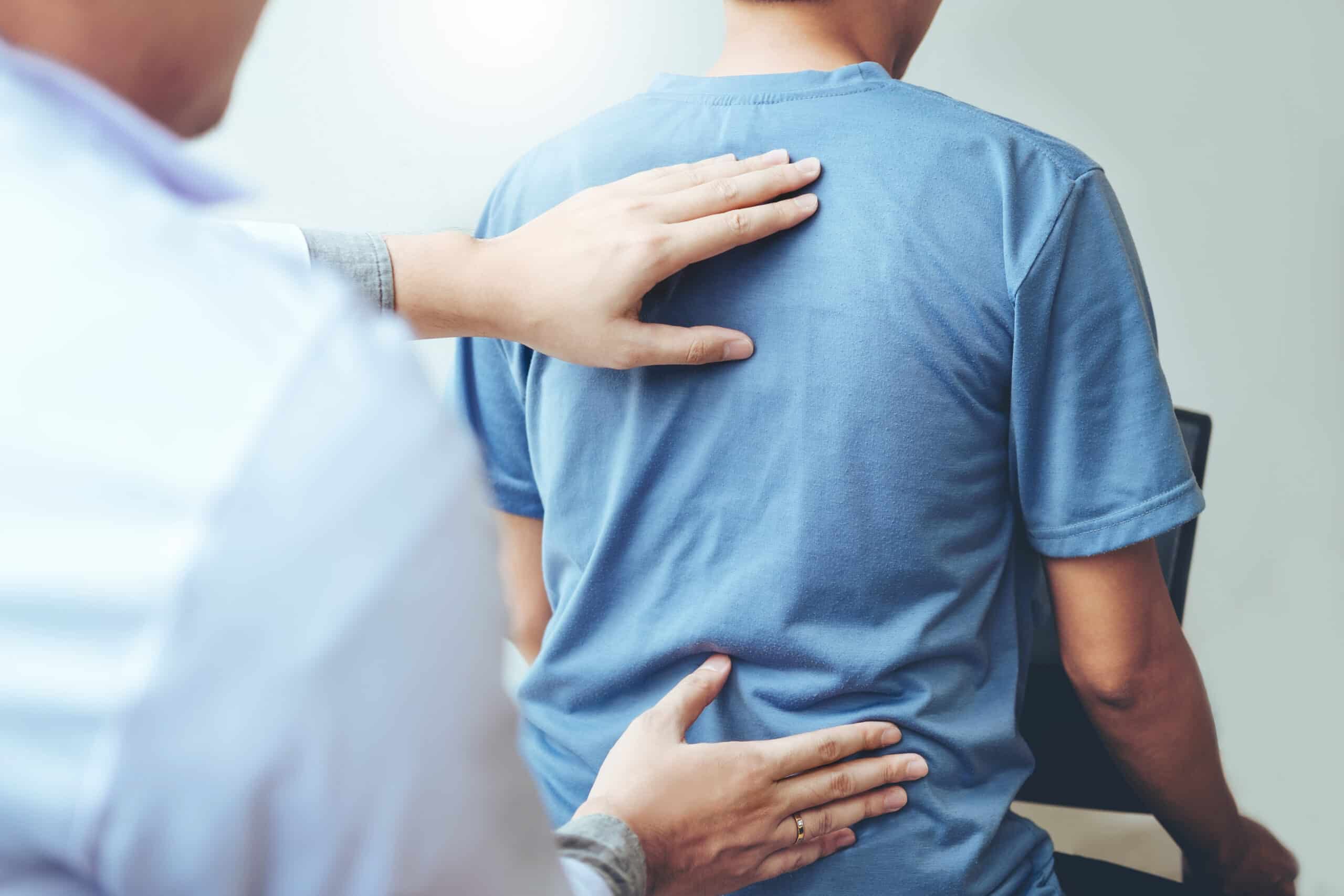
What Are The Signs & Symptoms of a Herniated Disc?
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of a herniated disc is essential for prompt intervention. Common indicators include:
Back Pain: Sharp or dull pain in the affected area of the spine.
Radiating Pain: Pain that extends into the arms or legs, depending on the disc location.
Numbness or Tingling: Sensations of numbness or tingling in the extremities.
Muscle Weakness: Weakness in specific muscles corresponding to the affected nerve.
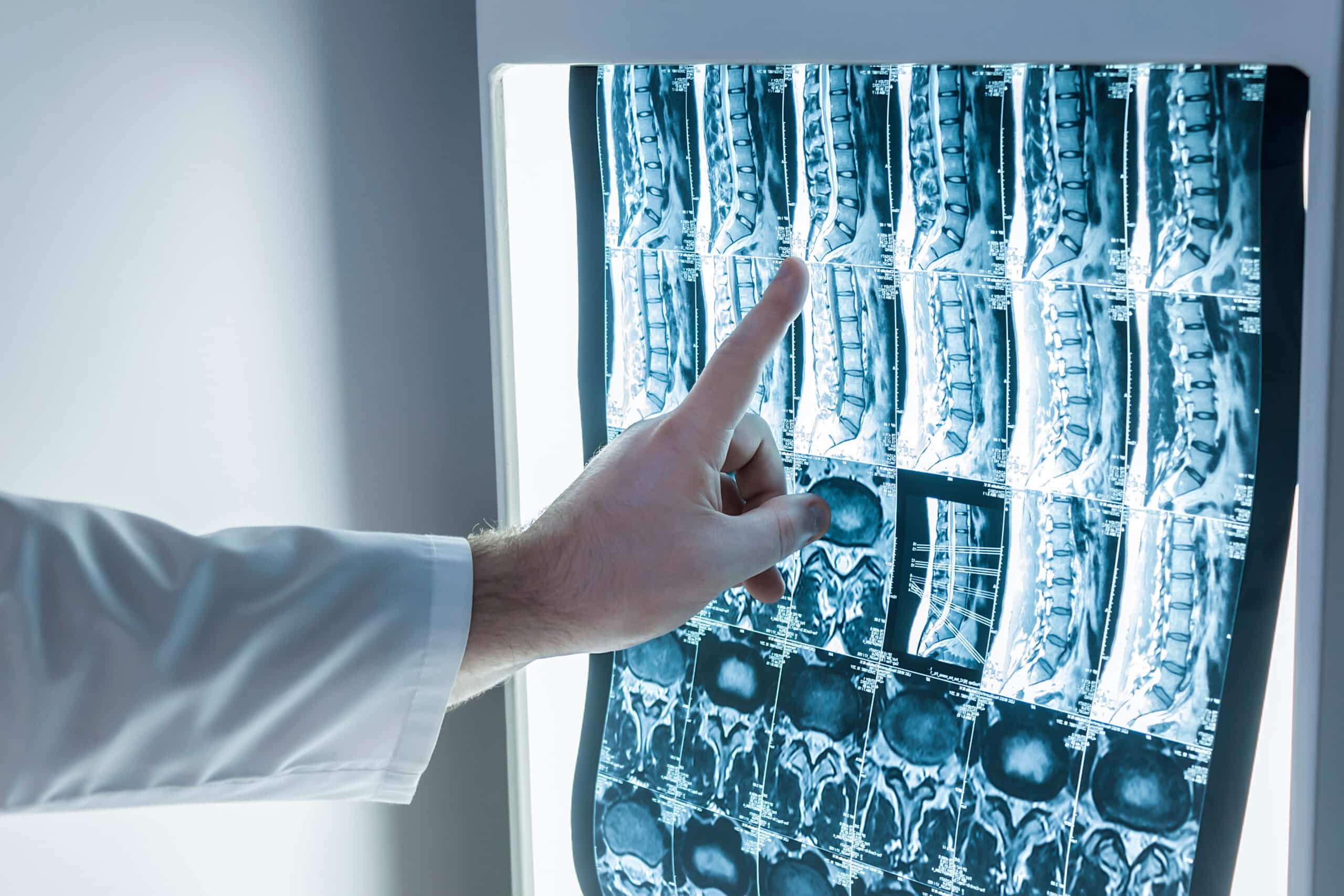
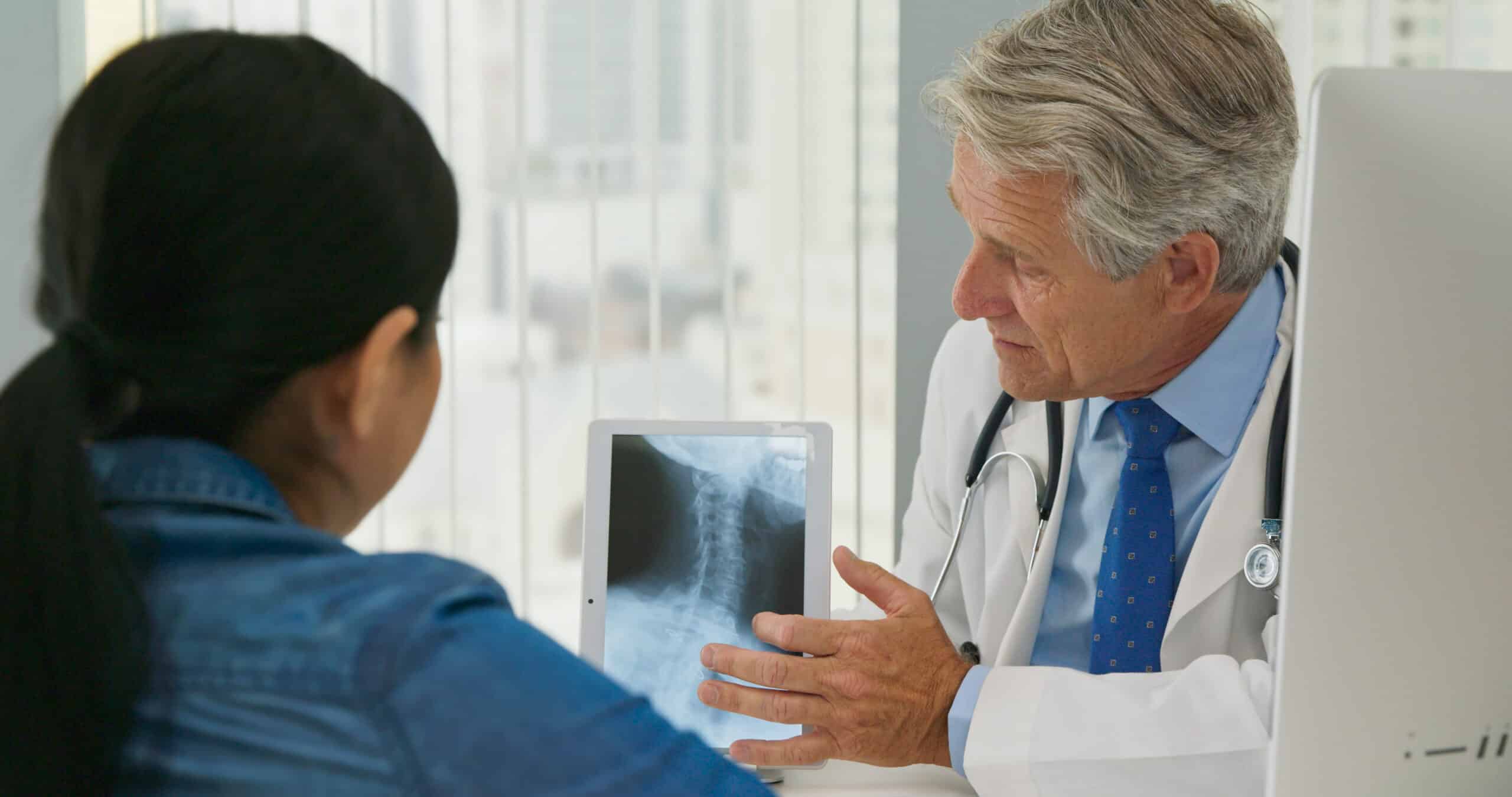
Testing & Diagnosis
Diagnosing a herniated disc involves a thorough examination. Diagnostic methods may include:
Medical History: Gathering information about symptoms, lifestyle, and past injuries.
Physical Examination: Assessing reflexes, muscle strength, and range of motion.
Imaging Studies: X-rays, MRI, or CT scans to visualize the spine and identify disc abnormalities.
What Are The Treatments For A Herniated Disc?
Treatment strategies for herniated discs aim to relieve symptoms and improve function. Common approaches include:
Rest and Physical Therapy: Allowing the disc to heal and strengthening surrounding muscles.
Medications: Pain relievers, muscle relaxants, and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Epidural Steroid Injections: Administered to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
Surgery: In severe cases, surgical procedures such as discectomy may be considered.